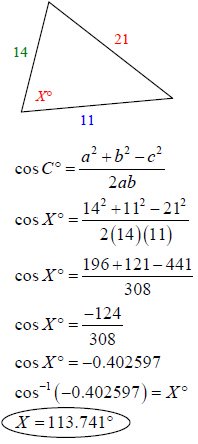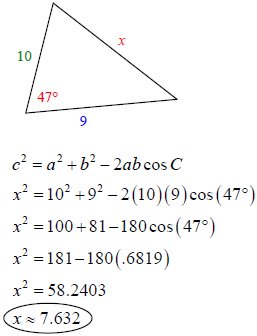|
|
|
|
The Law of Cosines (Cosine Rule)The law of cosines is used to finding missing sides and angles of triangles.
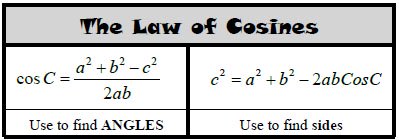
The Cosine Rule : c2 = a2 + b2 = 2abcosC Before you attempt to use the formula shown above, please be sure that you understand the basics of trigonometry first - please be certain you are able to:
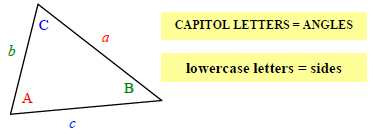
First, you must understand what the letters a, b, c and A, B, C represent in the formula. The corresponding letters (a & A, b & B, c & C) represent the side and the angle across from it. Please see the figure below.
Note: the letters used are arbitrary. As long as you match the side with the angle across from it, the formula will work!
The formula is listed in two forms: the standard form (used for sides) and a derivative of the standard form which makes it easier to colve for angles. Remember, to solve for an angle, you will eventually need to use the inverse function!
|
| . | ||
| Home │ Site Search │ Math Help Blog │ Help Keep GradeA Free | |
Written by Team GradeAmathhelp.com, all rights reserved. | ||